1. Basics of teaching
Teaching
- Involves the process of passing on knowledge, skills, and values to others.
- Acts as the cornerstone for individual growth and educational development.
Teaching Aptitude
- Refers to the inherent ability or potential to teach effectively.
- Measures how well a teacher can foster meaningful learning experiences and create an engaging classroom environment.
Teaching-Learning (T-L) Model
- A structured framework representing the dynamics of teaching and learning.
- Focuses on the interaction between teachers and students during the instructional process.
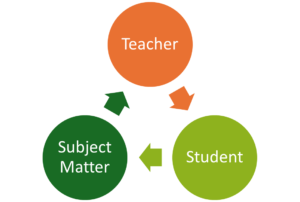
Triadic Nature of Teaching
Teaching is based on a three-part relationship involving:
- Teacher – The facilitator of learning.
- Student – The recipient and active participant in learning.
- Subject Matter – The content or knowledge being delivered.
Key Insights about Teaching and Learning
- Teaching and learning are closely interconnected processes.
- Teaching is fundamentally a social activity, involving interaction and communication.
- Learning, on the other hand, is a personal and internal process.
- While teaching requires the presence of learners, learning can still happen independently, without a teacher.
Q1. The Phrase T-L model of teaching implies that
[September-2020]
1. Teaching and learning are independent acts
2. Teaching and learning are integrally related acts
3. Teaching aims at learning
4. Teaching causes learning
Q2. Which of the following statements differentiate teaching from learning?
[December-2019]
(a) Teaching is a social act while learning is a personal act
(b) Teaching implies learning
(c) Teaching is like selling while learning is like buying
(d) Teaching can occur without learning taking place
(e) In teaching, influence is directed towards learning and learner, while in learning it is usually towards oneself
(1) ace
(2) abc
(3) bcd
(4) cde
Q3. Learning objectives mean
[June-2019]
(1) Learning experience
(2) Concise outcomes
(3) Academic achievement
(4) Intended learning outcomes
2. Types of Teaching Competencies
Personality and Attitude Competencies
- A positive mindset and adaptable personality.
- Strong internal drive and belief in one’s ability to influence outcomes (locus of control and self-efficacy).
- Logical reasoning and clarity in thought.
- Confidence paired with enthusiasm for teaching.
Behavioral or Work-Related Competencies
- Planning and Teaching: Designing structured lesson plans and delivering them effectively.
- Managing, Monitoring, and Communicating: Handling classroom activities, tracking student progress, and maintaining effective communication.
- Evaluating and Providing Feedback: Judging students’ performance and sharing helpful feedback for growth.
Substantive Competencies
- Subject Knowledge: Deep understanding of the topic being taught.
- Literacy Levels: Strong command of language and communication.
Style-Related Competencies
Dynamism and Flexibility: Adjusting teaching methods based on the classroom situation.
Organization and Orderliness: Maintaining a well-structured approach to lesson delivery.
Social Competencies
- Empathy: Being sensitive to students’ emotions and viewpoints.
- Social Skills: Nurturing healthy relationships and creating a positive learning environment.
Personal Competencies
- Self-Awareness: Recognizing one’s capabilities and limitations.
- Self-Regulation: Managing emotions and maintaining discipline.
- Motivation: Staying driven and inspiring students to reach their goals.
Q1. The Phrase T-L model of teaching implies that
[September-2020]
1. Teaching and learning are independent acts
2. Teaching and learning are integrally related acts
3. Teaching aims at learning
4. Teaching causes learning
Q2. Which of the following statements differentiate teaching from learning?
[December-2019]
(a) Teaching is a social act while learning is a personal act
(b) Teaching implies learning
(c) Teaching is like selling while learning is like buying
(d) Teaching can occur without learning taking place
(e) In teaching, influence is directed towards learning and learner, while in learning it is usually towards oneself
(1) ace
(2) abc
(3) bcd
(4) cde
Q3. Learning objectives mean
[June-2019]
(1) Learning experience
(2) Concise outcomes
(3) Academic achievement
(4) Intended learning outcomes
3. Phases Of Teaching
Pre-Active Phase (Planning Stage):
- Teacher prepares before entering the classroom.
- Sets specific learning objectives.
- Designs lesson plans tailored to student needs.
- Selects suitable teaching materials and resources.
- Aims to build a structured and organized lesson framework.
Interactive Phase (Delivery Stage):
- Actual teaching takes place.
- Teacher presents content and engages students.
- Encourages participation through discussions, activities, and demonstrations.
- Provides immediate feedback to students.
- Focus is on active learning and student involvement.
Post-Active Phase (Evaluation Stage):
- Conducted after the lesson concludes.
- Teacher assesses student performance through tests or assignments.
- Reviews the effectiveness of the lesson.
- Reflects on successes and areas for improvement.
- Uses feedback to enhance future teaching strategies.
Q1. What are the activities of teaching associated with its interactive stage?
[2023]
(a) Planning of lesson
(b) Determining learning outcomes
(c) Presenting the content interspersed with questions
(d) Providing feedback and probing, if need be
(e) Motivating and monitoring students tasks
(1) abc
(2) bcd
(3) acd
(4) cde
Q3. Match the column:
[2020]
A. Planning
B. Organizing
C. Motivation
D. Controlling
I. It involves feedback of results and follow up to compare accomplishments
II. It involves engagement in task relevant activities
III. It involves bringing together resources and people
IV. It involves setting goals and objectives
(1) A-IV B-III C-II D-I
(2) A-I B-II C-III D-IV
(3) A-II B-I C-IV D-III
(4) A-III B-IV C-I D-II
Q4. Match the column:
[2023]
| Domains of Teaching Responsibility | Components of Domains |
|---|---|
| A. Planning and preparation | IV. Setting instructional outcomes |
| B. Instruction | I. Communicating with students |
| C. Classroom Environment | II. Establishing a culture for learning |
| D. Professional Responsibilities | III. Reflecting on teaching |
(1) A-IV B-I C-III D-II
(2) A-IV B-I C-II D-III
(3) A-II B-IV C-I D-III
(4) A-II B-IV C-III D-I
