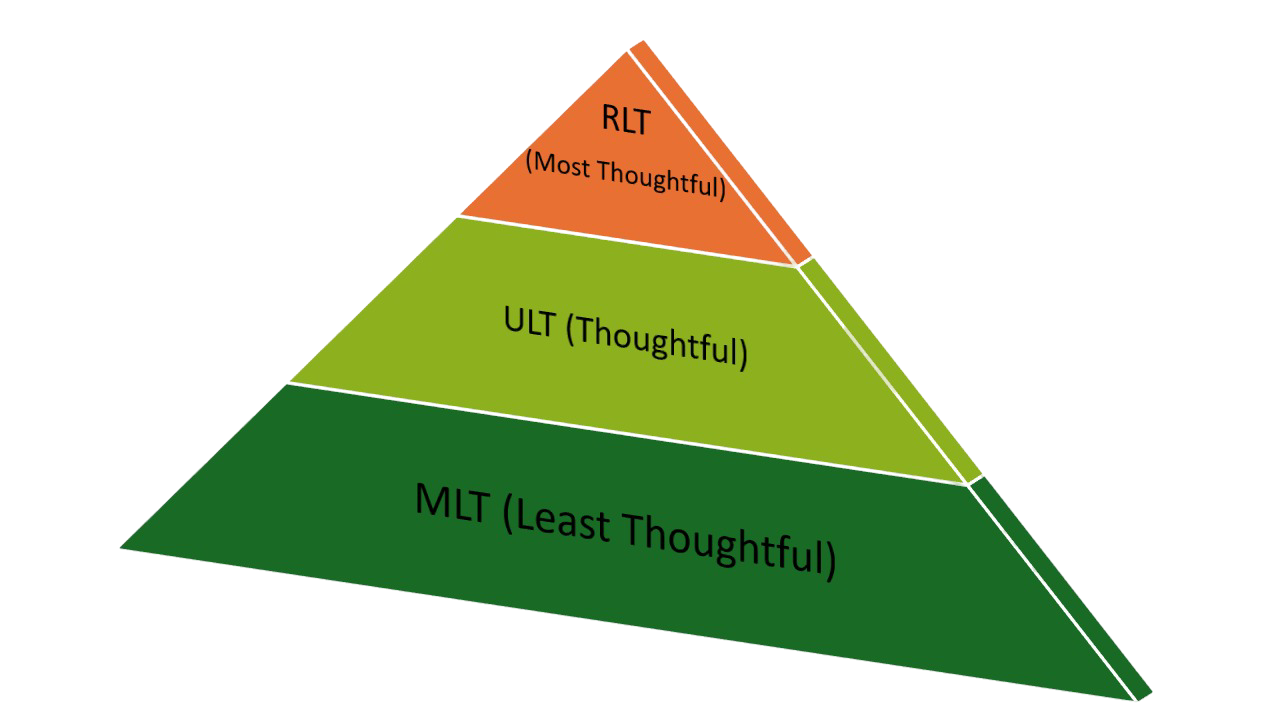
1. Levels of teaching
- Teaching progresses through different levels based on how students engage with and process new concepts.
- These levels help educators design effective teaching strategies tailored to students’ cognitive development.
- Initially proposed by Morris L. Biggie (1976), the framework includes:
- Memory Level
- Understanding Level
- Reflective Level
- Autonomous Development Level (added later)
1. Memory Level of Teaching (MLT)
Proponent: Johann Friedrich Herbart
Features:
- Focuses on rote memorization.
- Involves basic learning where students memorize facts without deep understanding.
- Examples: Learning the alphabet, multiplication tables, country capitals.
Key Components:
- Learning the material.
- Retaining the information.
- Recalling it when needed.
Objectives:
- Instill factual knowledge through repetition.
- Content is simple, structured, and easy to grasp.
Teaching Techniques:
- Repetition and drill-based learning.
- Use of visual aids like charts, flashcards, and audio-visual tools.
- Teacher-driven approach where students passively receive information.
Evaluation Methods:
- Oral or written tests to check memorization.
- Objective-type questions are preferred.
Suggestions for Teachers:
- Ensure content is useful and goal-oriented.
- Start with simpler materials, progressing to more complex ones.
- Incorporate memory tricks and visual tools.
- Organize lessons clearly and systematically.
- Use frequent assessments to monitor retention.
Movie Connection:
📽️ 3 Idiots – Chatur’s speech showcases rote memorization without comprehension, leading to a humorous mishap.
2. Understanding Level of Teaching (ULT)
Proponent: Morrison
Features:
- Goes beyond memorizing to foster real understanding.
- Students grasp concepts and their underlying principles.
- Example: Instead of just knowing that plants need sunlight, students explore why they need it.
Objectives:
- Enable students to apply concepts using examples and comparisons.
- Encourage thoughtful engagement with wider and deeper subject matter.
Teaching Techniques:
- Lectures, discussions, and demonstrations.
- Use of models, charts, videos, and case studies.
- Balanced interaction between teacher and student.
- Active student participation encouraged.
Evaluation Methods:
- Objective or descriptive tests.
- Field visits, case study analysis, and project work.
Suggestions for Teachers:
- Foster a highly interactive environment.
- Motivate students to explore deeper questions.
- Use engaging aids to keep students interested.
- Present information logically to aid understanding.
Movie Connection:
📽️ Om Shanti Om – Sandy studies and practices deeply to understand and emulate Shantipriya, reflecting true comprehension and application.
3. Reflective Level of Teaching (RLT)
Proponent: Hunt
Features:
- Encourages students to apply knowledge to real-life situations.
- Focus is on problem-solving, critical thinking, and independent decision-making.
- Considered the most advanced and thoughtful level.
Objectives:
- Promote analytical and independent thinking.
- Develop decision-making and real-world problem-solving abilities.
Teaching Techniques:
- Student-led activities like debates, case studies, internships, and live projects.
- Unstructured, dynamic classroom environments.
- Teacher plays a facilitative, democratic role.
Evaluation Methods:
- Project-based assessment.
- Reflective journals, presentations, and creative assignments.
Suggestions for Teachers:
- Guide students subtly without dominating.
- Encourage self-directed learning.
- Provide feedback and foster critical dialogue.
Movie Connection:
📽️ MBA course setting – Students solve real-world case studies, simulating reflective and analytical learning.
4. Autonomous Development Level
Proponent: Morris L. Biggie
Features:
- Learning occurs naturally, led entirely by the learner.
- Students pursue topics of interest on their own.
- Teachers act only as guides, offering support when needed.
Objectives:
- Cultivate lifelong learners who explore independently.
- Emphasize internal motivation and curiosity.
Example:
- A student independently researching a hobby or subject without formal instruction.
Movie Connection:
📽️ English Vinglish – Shashi learns English by enrolling in a course herself, showing self-motivated and independent learning.
Summary Comparison: MLT vs. ULT vs. RLT
| Level | Focus | Example |
|---|---|---|
| MLT | Memorizing facts | Knowing a lion is a big cat in Africa. |
| ULT | Understanding reasons | Knowing why lions roar. |
| RLT | Applying knowledge | Thinking about conservation of lions due to human impact. |
Q1. Which of the following can be considered as the component of development of ability of critical and logical thinking?
[2024]
(A) To identify the problems
(B) To analyse the problems
(C) To establish subjective truths
(D) To select relevant facts and principles
(E) To draw inferences and conclusions
(1) A and C only
(2) A, B and C only
(3) A, B and D only
(4) A, B, D and E only
Q2. Which of the following levels of teaching involves the highest order thinking skills?
[2023]
(1) Memory level
(2) Understanding level
(3) Reflective level
(4) All levels involve similar thinking skills
Q3. Statement I: Teaching at the understanding level involves encouraging students to think critically and reflect on their learning experiences.
Statement II: Teaching at the memory level involves rote memorization and does not encourage critical thinking.
[2023]
(1) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(2) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(3) Statement I is true but Statement II is false
(4) Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Q4. Statement I: The objective of the memory level of teaching is to develop rational and critical thinking among students.
Statement II: The objective of the reflective level of teaching is the ability to develop independent thinking and decision making among students.
[2023]
(1) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(2) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(3) Statement I is true but Statement II is false
(4) Statement I is false but Statement II is true
